
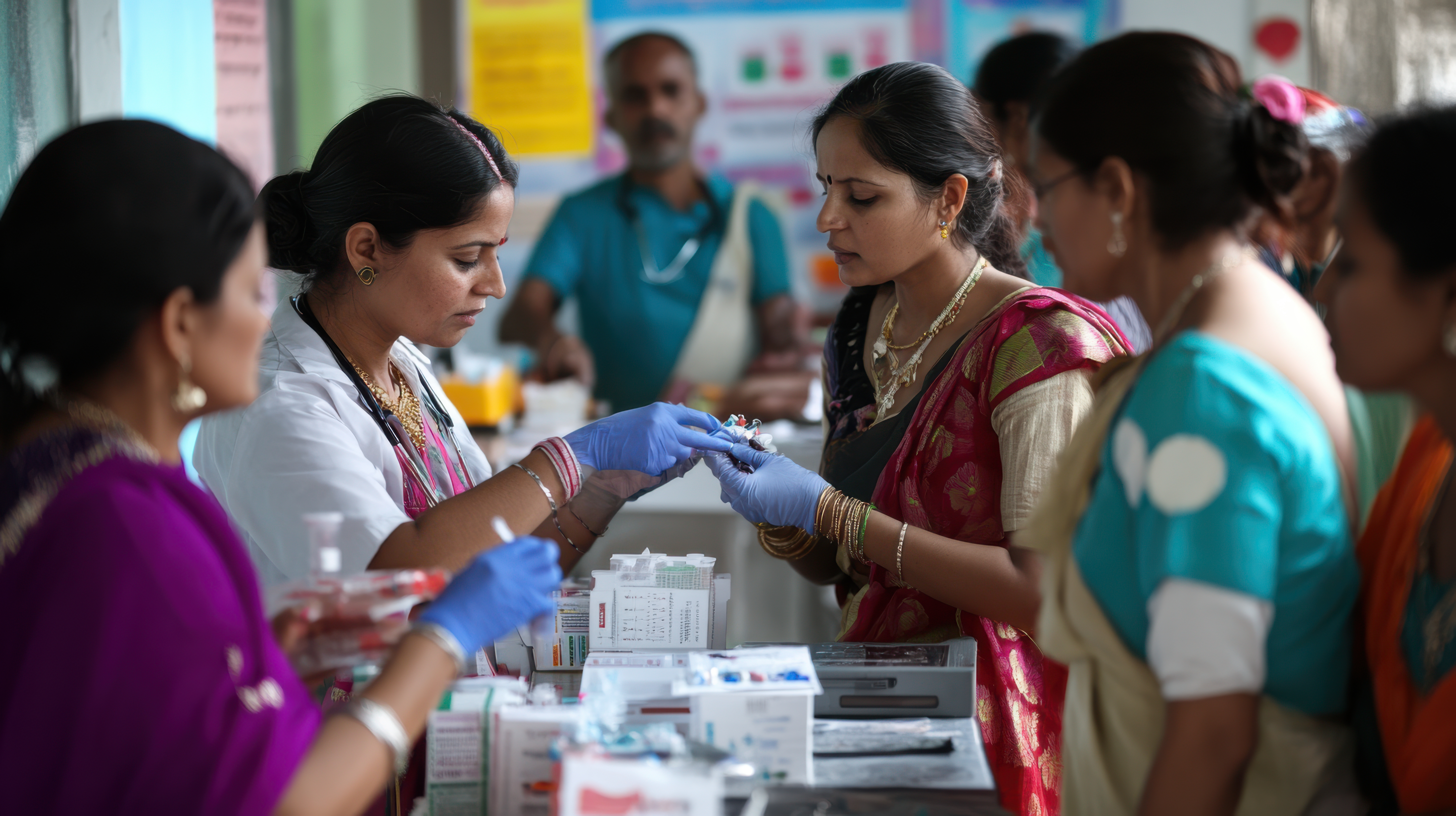
Strengthening Primary Health Care Centers: Efforts to strengthen primary health care centers would involve discussions around increasing funding, improving access to essential healthcare services, and enhancing the capabilities of healthcare workers. This might involve commitments to recruit and train more healthcare professionals, upgrade facilities, and ensure a steady supply of medical resources and equipment.
Universal Health Coverage: Universal health coverage (UHC) aims to ensure that all individuals and communities have access to the quality healthcare services they need without suffering financial hardship. . This could include sharing strategies for expanding healthcare access, improving health insurance systems, reducing out-of-pocket expenses, and prioritizing health equity.
Healthcare Infrastructure: During the G20 Summit, leaders might emphasize the importance of developing and maintaining modern healthcare facilities, including hospitals, clinics, and laboratories.
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)Antimicrobial resistance is a global health concern where microorganisms become resistant to the drugs designed to control them, leading to more difficult-to-treat infection. Leaders might endorse policies to promote responsible antibiotic use, support research and development of new antibiotics, and enhance surveillance and data sharing to monitor resistance patterns globally.
Research and Development Collaborations: Leaders at the G20 Summit could encourage collaborative research and development initiatives aimed at addressing global health threats. This might involve sharing resources, expertise, and data to accelerate the discovery and development of medical countermeasures such as vaccines, treatments, and diagnostics.
Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between governments, international organizations, and the private sector is key to strengthening the pharmaceutical sector. The G20 Summit could encourage the formation of public-private partnerships to leverage expertise, resources, and innovation for improved access to medical countermeasures.
Digital Health : The G20 Summit could focus on building and enhancing digital health infrastructure, including electronic health records, telemedicine platforms, and interoperable systems that enable seamless data exchange across borders. This infrastructure could facilitate better patient care coordination, reduce duplication of tests, and enable health data access for medical travellers.
Impact of Summit on Climate Change and Health: Countries may discuss and share strategies for adapting healthcare systems to changing climate conditions. This could include strengthening healthcare infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events, designing public health campaigns to raise awareness about climate-related health risks, and creating early warning systems for disease outbreaks.
Global health emergencies: The G20 could stress the importance of global health preparedness for future emergencies. This might involve establishing international frameworks for early detection, rapid response, and coordinated efforts. Leaders might discuss the need to develop and share comprehensive pandemic response plans that outline actions, responsibilities, and resource allocation during health crises.
Medical Tourism: The summit could address travel and visa facilitation for patients seeking medical treatment abroad. Simplified visa processes and travel arrangements could make medical tourism more accessible.
Cultural Preservation: The G20 could emphasize the preservation of cultural heritage related to traditional medicines. This might involve protecting indigenous knowledge and practices and ensuring they are not lost over time.
Recent Posts

Get Free
Consultations
Special Advisors
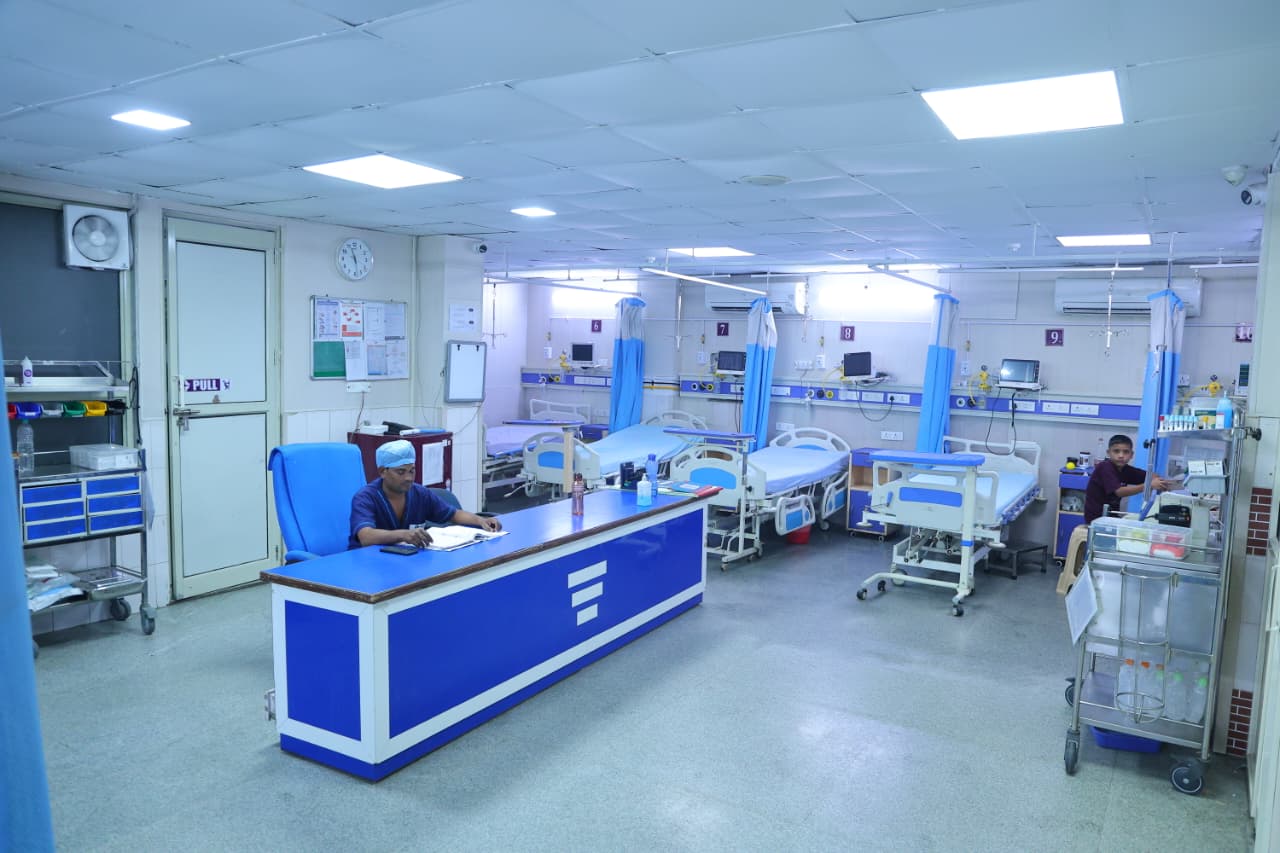







Future of Hospital Design in India