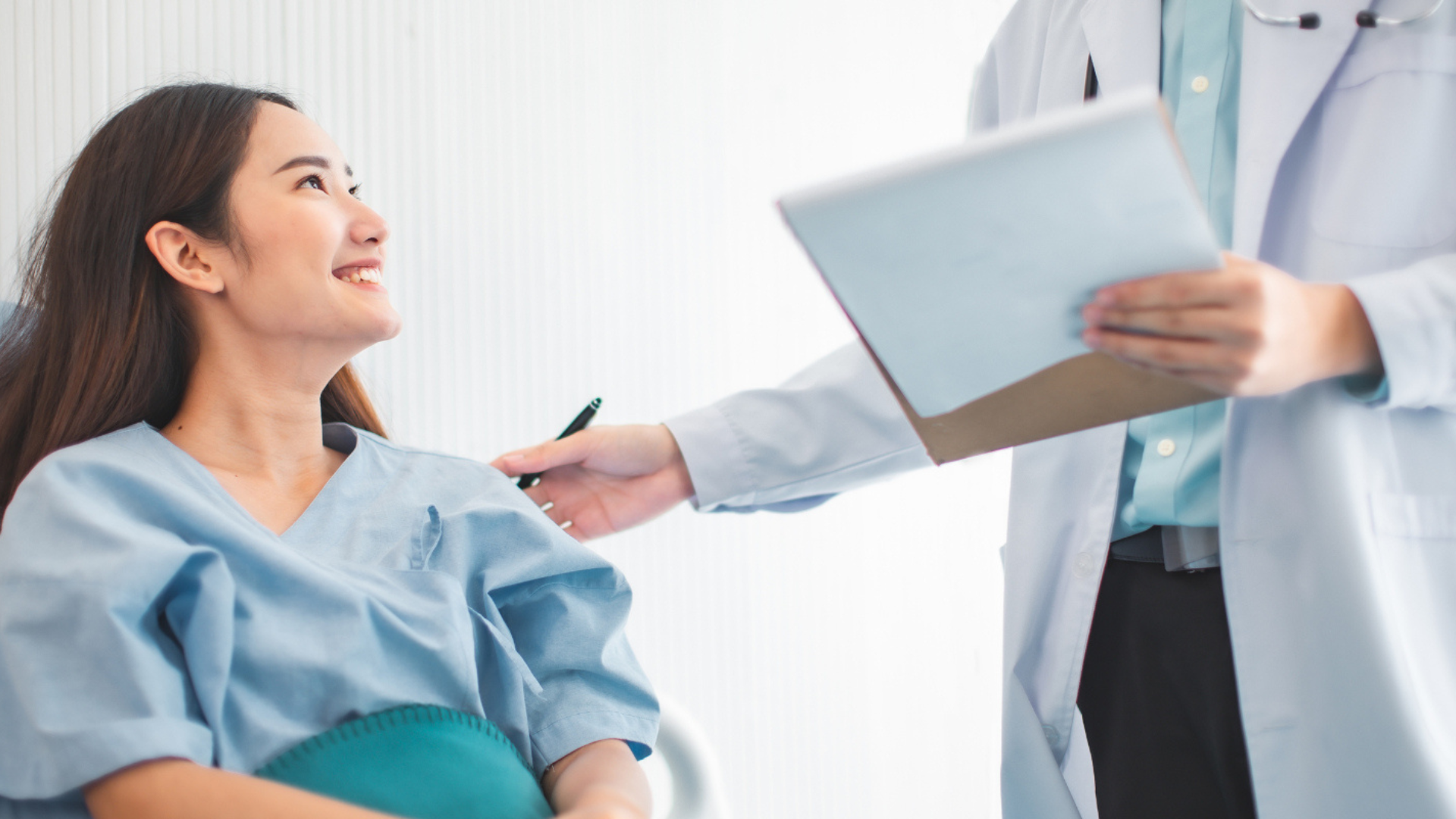

The shift from a physician-centric approach to patient-centric care represents a broader movement in healthcare that recognizes the importance of focusing on the needs, preferences, and experiences of patients.
Following factors contribute to this shift:
Empowerment and Informed Decision-Making: Patients today are more informed about their health due to increased access to information through the internet. This has led to a desire for a more collaborative relationship with healthcare providers, where patients actively participate in decision-making about their care.
Patient Rights and Autonomy: There is a growing recognition of patients' rights and autonomy. Patients are seen as partners in their healthcare journey, with the right to be informed, involved, and respected in decisions related to their health.
Holistic Approach to Health: The understanding of health has evolved to encompass the overall well-being of individuals. Patient-centric care takes a holistic approach, considering the patient's values, lifestyle, and social context.
Focus on Outcomes and Quality of Life: The emphasis in healthcare is shifting from a focus solely on treating diseases to achieving better patient outcomes and improving quality of life. This involves understanding and addressing the physical, emotional, and social aspects of health.
Advancements in Technology: Technological advancements, such as electronic health records, telemedicine, and health apps, enable greater patient engagement. Patients can access their health information, communicate with healthcare providers, and actively manage their health.
Cultural and Societal Changes: Societal expectations and cultural shifts have influenced the way healthcare is delivered. There is a greater awareness of the importance of patient satisfaction, and healthcare systems are adapting to meet these expectations.
Value-Based Care Models: Healthcare systems are increasingly moving towards value-based care models, where the focus is on delivering high-quality care with an emphasis on patient outcomes rather than the volume of services provided. This shift aligns with the principles of patient-centric care.
Conclusion
The shift to patient-centric care reflects a recognition that healthcare should be more than just treating illnesses—it should be about improving the overall health and well-being of individuals in a way that respects their values, preferences, and autonomy.
Recent Posts

Get Free
Consultations
Special Advisors







Future of Hospital Design in India